Fascisterne: Meaning, History, Ideology, and Modern Relevance
The term fascisterne is often searched by people who want to understand its meaning, historical background, political ideology, and relevance in today’s world. The word is commonly used in Scandinavian and European contexts to refer to fascists or fascist movements, either historically or in modern political discussion. This article explains fascisterne in clear, human language, covering its origins, beliefs, historical examples, impact on society, criticism, and why the term still appears in news, education, and public debate.
What Does Fascisterne Mean?
Fascisterne is a plural term that generally refers to fascists—people or groups who follow or support fascist ideology.
Simple Definition
Fascisterne refers to:
- Individuals who believe in fascism
- Political movements based on fascist ideas
- Historical or modern groups linked to authoritarian nationalism
The term is often used critically rather than neutrally.
Origin of the Term Fascisterne
To understand fascisterne, it is important to understand where fascism comes from.
Roots of Fascism
Fascism originated in Europe in the early 20th century.
Historical Background
- Emerged after World War I
- Grew during periods of economic crisis and political instability
- Promoted strong leadership and national unity
The ideology appealed to people seeking order and identity during uncertain times.
Meaning of the Word Fascism
Etymology
The word “fascism” comes from the Latin word fasces, a symbol of authority and unity.
Symbolic Meaning
- Strength through unity
- Power concentrated in authority
- Obedience to the state
Core Beliefs of Fascisterne
Fascisterne follow a set of beliefs that define fascist ideology.
Strong Nationalism
Key Idea
The nation is placed above the individual.
- Emphasis on national identity
- Glorification of history and tradition
- Hostility toward perceived outsiders
Authoritarian Leadership
Power Structure
- Strong central leader
- Limited political opposition
- Suppression of dissent
Democracy is often viewed as weak or inefficient.
Anti-Democratic Values
Why Democracy Is Rejected
- Seen as divisive
- Considered slow and unstable
- Replaced by centralized control
Militarism and Strength
Belief System
- Military power is valued
- Violence may be justified for national goals
- Strength is admired over compromise
Control of Media and Expression
Information Management
- State-controlled media
- Censorship of opposing views
- Propaganda used to shape public opinion
Economic Views of Fascisterne
Fascism does not fit neatly into traditional economic categories.
State-Controlled Capitalism
How It Works
- Private ownership may exist
- State controls key industries
- Economy serves national goals
Opposition to Socialism and Liberalism
Ideological Position
- Rejects class struggle
- Opposes individual freedoms emphasized by liberalism
- Promotes unity over equality
Historical Examples of Fascisterne

Understanding history helps explain why fascism is widely criticized.
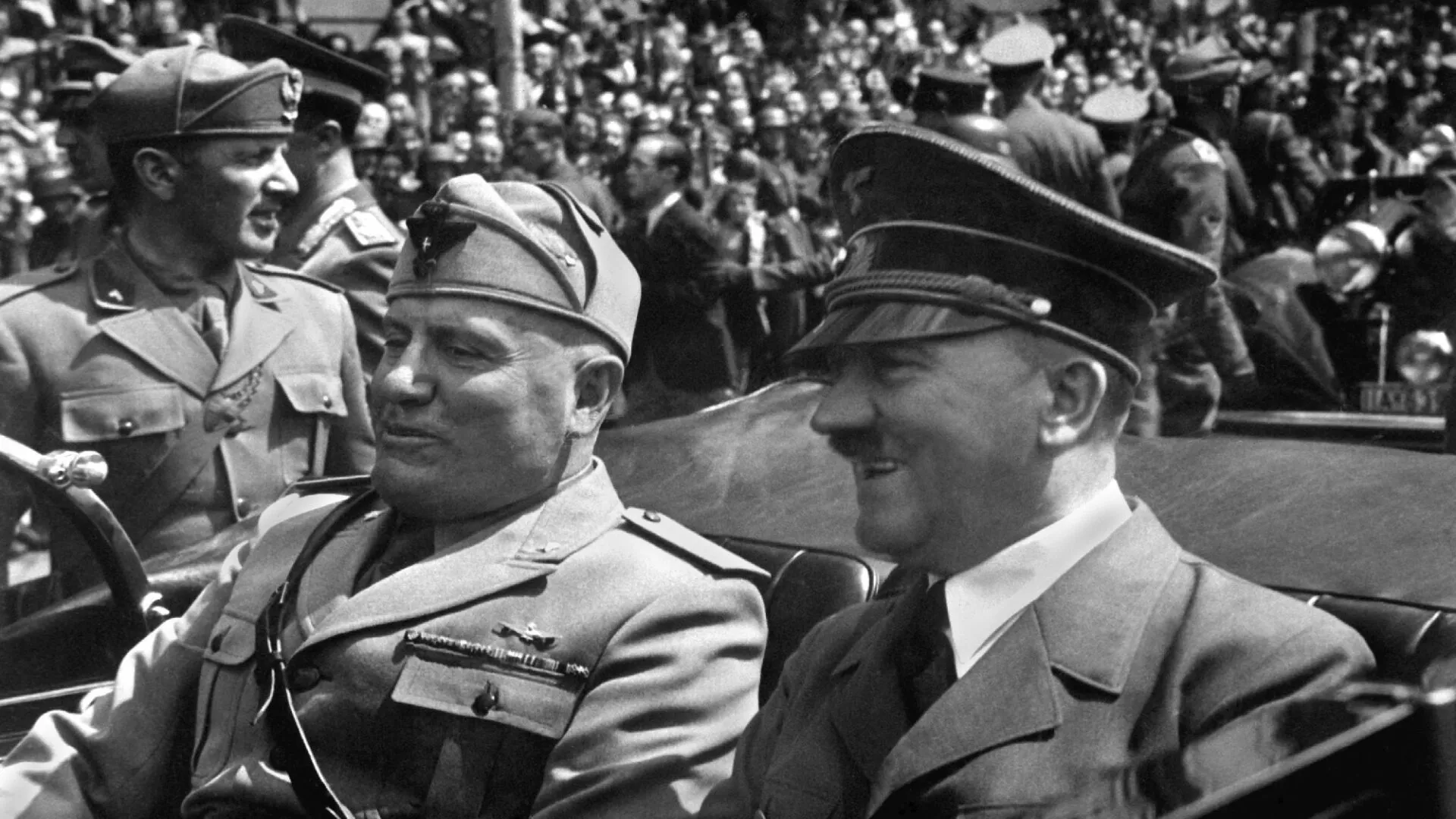
Fascist Italy
Overview
- One of the first fascist states
- Emphasized nationalism and expansion
- Controlled media and opposition
Nazi Germany
Extreme Form of Fascism
- Combined fascism with racial ideology
- Led to massive human rights violations
- Caused global conflict and genocide
Other European Fascist Movements
Examples
- Spain under authoritarian rule
- Smaller fascist parties across Europe
These movements shared similar ideas with local variations.
Impact of Fascisterne on Society
Fascist movements left deep scars on societies.
Loss of Freedoms
Consequences
- Free speech restricted
- Political opposition punished
- Independent institutions weakened
Human Rights Violations
Historical Reality
- Persecution of minorities
- Use of violence and imprisonment
- Discrimination enforced by law
War and Destruction
Global Impact
- Fascist expansion led to war
- Millions of lives lost
- Long-term social and economic damage
Why Fascisterne Are Widely Criticized
Fascism is broadly rejected due to its outcomes and values.
Oppression and Fear
Reason
Control is maintained through fear, not consent.
Lack of Accountability
Issue
Leaders are rarely held responsible for abuses.
Suppression of Diversity
Problem
Differences are seen as threats rather than strengths.
Destruction of Democratic Institutions
Impact
Democracy is replaced by rigid authority.
Fascisterne in Modern Times
Although classic fascist regimes ended, the term still appears today.
Modern Usage of the Term
How It Is Used
- To describe extremist political groups
- As criticism in political debate
- In academic and historical analysis
Neo-Fascism
Definition
Modern movements inspired by fascist ideas.
- Often avoid the fascist label
- Adapt ideology to modern contexts
- Use nationalism and populism
Online Influence
Digital Era
- Use of social media for messaging
- Spread of propaganda and misinformation
- Recruitment through online communities
Difference Between Fascisterne and Other Ideologies
Understanding differences avoids confusion.
Fascism vs Democracy
Key Difference
Democracy values pluralism; fascism demands unity under authority.
Fascism vs Communism
Contrast
Both can be authoritarian, but fascism emphasizes nationalism while communism focuses on class equality.
Fascism vs Conservatism
Important Distinction
Traditional conservatism supports institutions and law, while fascism seeks total control.
Why People Are Curious About Fascisterne
Search interest reflects social awareness.
Educational Reasons
Students and Researchers
Learning history and political theory.
News and Media
Current Events
Term appears in discussions about extremism.
Political Debate
Public Discourse
Used to criticize authoritarian behavior.
Cultural and Historical Interest
Understanding the Past
Helps prevent repetition of mistakes.
How Fascisterne Are Studied Today
Modern study focuses on prevention and understanding.
Academic Analysis
Focus Areas
- Causes of radicalization
- Social conditions that enable extremism
- Warning signs of authoritarianism
Civic Education
Goal
Promote democratic values and critical thinking.
Historical Memory
Importance
Remembering victims and consequences.
How Societies Respond to Fascist Ideas
Democratic societies actively resist fascism.
Legal Protections
Measures
- Constitutional safeguards
- Protection of free speech and rights
Education and Awareness
Strategy
Teaching history to younger generations.
Media Responsibility
Role
Fact-checking and countering misinformation.
Community Engagement
Impact
Encouraging inclusion and dialogue.
Misuse of the Term Fascisterne
The term is sometimes overused.
Political Labeling
Concern
Used loosely to attack opponents.
Dilution of Meaning
Risk
Overuse weakens historical significance.
Importance of Accuracy
Advice
Use the term carefully and responsibly.
Lessons from the History of Fascisterne
History provides clear warnings.
Democracy Requires Protection
Lesson
Freedoms are not guaranteed without vigilance.
Economic and Social Stability Matters
Insight
Crisis can fuel extremism.
Critical Thinking Is Essential
Reason
Propaganda thrives where questioning is discouraged.
Why Understanding Fascisterne Matters Today
Knowledge helps societies stay resilient.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Benefit
Early awareness prevents escalation.
Defending Democratic Values
Outcome
Strong institutions protect freedom.
Promoting Human Rights
Goal
Ensure dignity and equality for all.
Conclusion
Fascisterne refers to individuals or movements connected to fascist ideology—an authoritarian, nationalist system that has caused immense harm throughout history. While fascism emerged during specific historical crises, its ideas continue to resurface in modern forms, making understanding this concept more important than ever. By learning about the beliefs, history, and consequences of fascisterne, societies can better recognize threats to democracy, protect human rights, and promote inclusive, peaceful political systems. Education, awareness, and critical thinking remain the strongest defenses against the return of destructive ideologies.